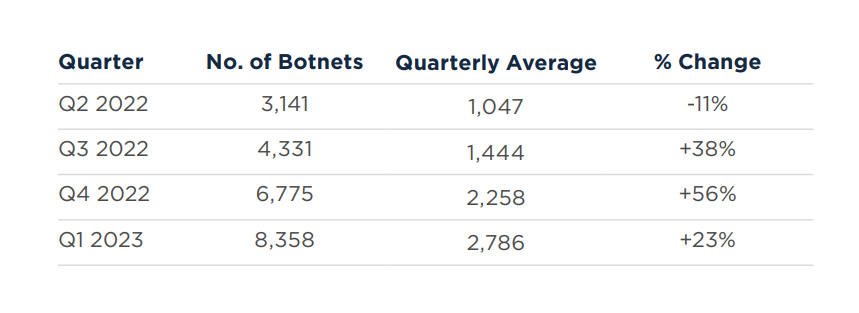
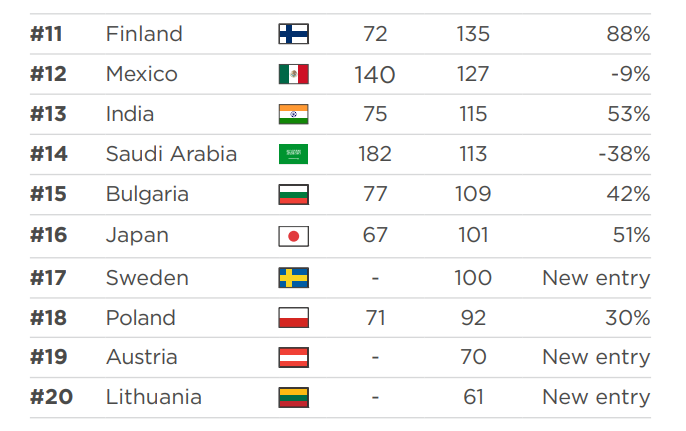
According to botnet threat update report Q1 2023 from Spanhaus, The number of botnet command and control (C&C) servers continued to escalate in the first quarter of 2023 by +23%. Across Europe, activity increased, but as per the norm, the United States, China, and Russia led the way. In addition to Cobalt Strike and Qakbot contributing to the increase in numbers, there was a growing popularity in credential stealers, none more so than that of Record Breaker, which experienced a massive 899% surge.
Geolocation of botnet C&Cs, Q1 2023
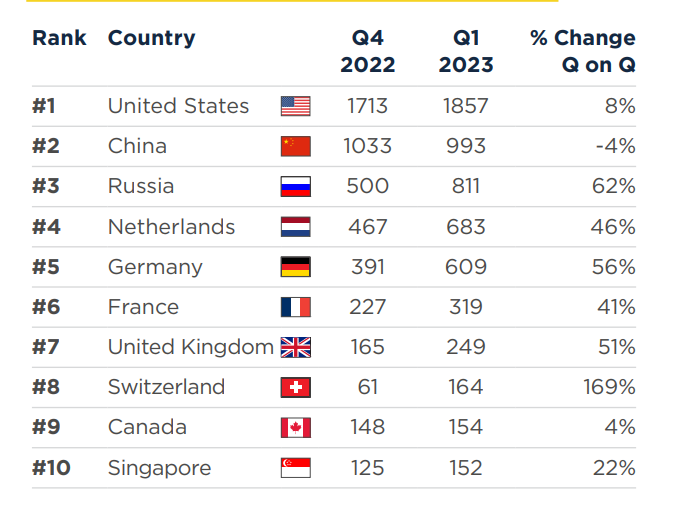
The U.S.A., China, and Russia remain the botnet threat superpowers
There was no change this quarter in the top three countries listed. While the U.S.A and China experienced minimal percentage changes, +8% and -4%, respectively, Russia witnessed a sizable 62% increase in botnet C&Cs. However, the award for the most significant growth in Q4 goes to Switzerland, with a whopping 169% surge.
Botnet threat increases across Europe
Another quarter – another set of increases across Europe relating to botnet C&C activity. This quarter, every new Top 20 entry is based in Europe: Sweden (#17), Austria (#19), and Lithuania (#20). Meanwhile, of the countries listed that suffered an uplift in botnet C&Cs this quarter, over 50% were based in Europe as per the botnet threat update report.
Top 20 locations of botnet C&Cs
You may also read: How to maintain a clean email list
What are botnet command & controllers?
A ‘botnet controller,’ ‘botnet C2’ or ‘botnet command & control’ server is commonly abbreviated to ‘botnet C&C.’ Fraudsters use these to both control malware-infected machines and extract personal and valuable data from malware-infected victims. Botnet C&Cs play a vital role in operations conducted by cybercriminals who are using infected machines to send out spam or ransomware, launch DDoS attacks, commit e-banking fraud or click-fraud, or mine cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin. Desktop computers and mobile devices, like smartphones, aren’t the only machines that can become infected. There is an increasing number of devices connected to the internet, for example, the Internet of Things (IoT), devices like webcams, network attached storage (NAS), and many more items. These are also at risk of becoming infected.
